LoRa (Long Range)
is a patented digital wireless data communication IoT technology
developed by Cycleo of Grenoble, France. It was acquired by Semtech in
2012, which holds the IP for LoRa transmission methodology.
LoRa
transmits over license-free sub-gigahertz radio frequency bands like
169 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz (Europe) and 915 MHz (North America). LoRa
enables very-long-range transmissions (more than 10 km in rural areas)
with low power consumption.
The
technology is presented in two parts — LoRa, the physical layer, and;
the communication protocol built upon the underlying LoRa physical
layer. The communication layer may be LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area
Network), an open source communication protocol defined by the LoRa
Alliance consortium; or may be Symphony Link, another open source
communication protocol defined by a company called Link Labs.
Thus, LoRaWAN™
defines the communication protocol and system architecture for the
network, while the LoRa® physical layer enables the long-range
communication link. LoRa WAN communication protocol
ensures reliable communication, secure communication and adds additional
headers to the data packets.
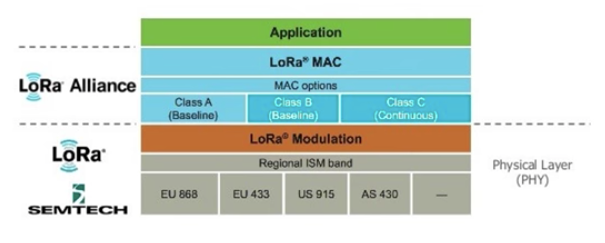
The LoRaWAN communication protocol is defined by the LoRa Alliance, a non-profit technology alliance of more than 500 member companies, committed
to enabling large scale deployment of Low Power Wide Area Networks
(LPWAN) IoT through the development, and promotion of the LoRaWAN open
standard.
The first LoRaWAN standard was announced by the LoRa Alliance in June 2015. In 2017 LoRaWAN specification 1.1 was released.
LoRa
and LoRaWAN permit inexpensive, long-range connectivity for IoT devices
in rural, remote and offshore industries. They are typically used in
mining, natural resource management, renewable energy, transcontinental
logistics, and supply chain management.
LoRaWAN
is the most adopted type of LPWAN, and promises ubiquitous connectivity
in outdoor IoT applications, while keeping network structures, and
management, simple.
LoRa and LoRaWAN Network Topology
LoRaWAN network architecture is deployed in a star-of-stars topology (vs. mesh topology eg. Zibgee).
The
LoRaWAN networks laid out in a star-of-stars topology have base
stations relaying the data between the sensor nodes and the network
server.
Communication
between the sensor nodes and the base stations goes over the wireless
channel utilizing the LoRa physical layer, whilst the connection between
the gateways and the central server are handled over a backbone
IP-based network.
- End Nodes transmit directly to all gateways within range, using LoRa.
- Gateways relay messages between end-devices and a central network server using IP.
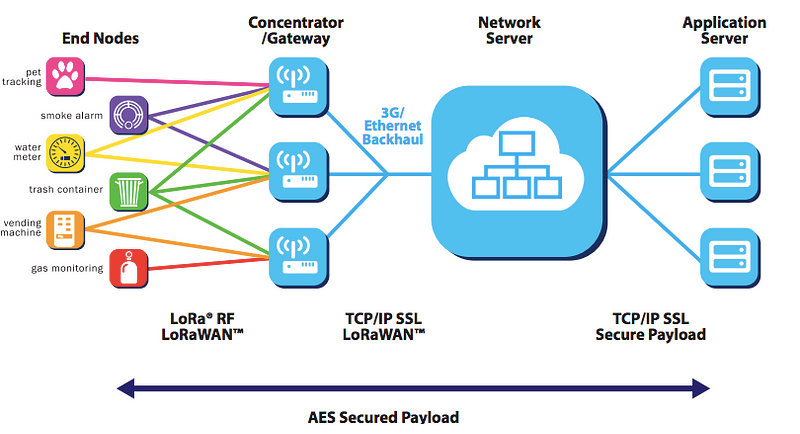
End NodesThe End Nodes are LoRa embedded sensors. The nodes typically have,
- Sensors (used to detect the changing parameter eg. temperature, humidity, accelerometer, gps),
- LoRa transponder to transmit signals over LoRa patented radio transmission method, and
- optionally a micro-controller (with on board Memory).
The
sensors may connect to the LoRa transponder chip, or the sensor may be
an integrated unit with the LoRa transponder chip embedded.
It
is possible to program the micro-controllers in micro-Python or
micro-Javascript. This allows developers to use the data from sensors
like accelerometers, temperature, etc. and implement certain use cases
eg. Fall detection algorithms may be implemented by programming the
micro controller based on the inputs from the accelerometer and other
sensors.
The
LoRaWAN end nodes(sensors) typically use Low Power and are battery
powered (Class A and Class B). LoRa embedded sensors that run on
batteries that can typically last from 2–5 years. The LoRa sensors can
transmit signals over distances from 1km — 10km.
GatewaysThe
LoRa sensors transmit data to the LoRa gateways. The LoRa gateways
connect to the internet via the standard IP protocol and transmit the
data received from the LoRa embedded sensors to the Internet i.e. a
network, server or cloud.
The
Gateways devices are always connected to a power source. The Gateways
connect to the network server via standard IP connections and act as a
transparent bridge, simply converting RF packets to IP packets and vice
versa.
Network ServersThe
Network servers can be cloud based platform solutions like The Things
Network (TTN) or LoRIOT. The network servers connect to the gateways and
de-dup data packets, and then routes it to the relevant application.
The network servers can be used for both uplink (i.e. sensor to
application) or downlink (i.e. application to sensor) communication.
The
Things Network Network server has a Router, Broker and Handler, which
processes the data packets from the LoRaWAN gateway. It also has an AWS
Bridge that connects TTN to the AWS IOT platform.
Application Servers
The Application can typically be built over IoT platforms like AWS IoT using Lambda, DynamoDb or S3 services.
The Application can typically be built over IoT platforms like AWS IoT using Lambda, DynamoDb or S3 services.
For earlier information ,visit
LPWAN - Fundamentals of IoT (Part1)
Source: Internet



0 comments:
Post a Comment